Emotional Marketing That Customers Actually Feel
A great product is forgettable if it never makes anyone feel something. This guide turns emotion into a repeatable system: pick one core feeling, tell a true story, show proof, and measure changes in memory, behavior, and pipeline.

Why Emotional Marketing Works
What we mean by emotional marketing
Design brand moments that trigger meaningful feelings; so people remember you, trust you, and act. Not manipulation. Relevance with the heart.
The science in one minute
Emotion → memory. Emotional arousal engages the amygdala, which helps “stamp” experiences into longer-term memory; why stories and moments beat spec sheets.
Needs → motivation. Map messaging to human needs (safety, belonging, esteem, growth) so your offer meets the moment.
Motivators → loyalty. When brands connect to deep motivators (feel secure, belong, stand out), customers become more valuable over time.
Theories behind emotional marketing
Maslow’s Needs
Use needs as a mapping tool: Safety → Belonging → Esteem → Self-actualization. Align copy, offer, and proof with the need your audience is solving right now.
Plutchik’s Emotions
Eight primary emotions: joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger, anticipation, plus intensity and blends. Pick one to lead a campaign; design visuals, pacing, color, and sound to support it.
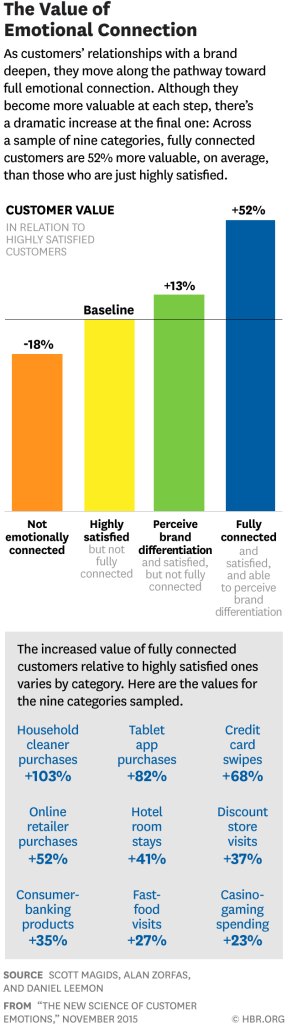
The Business Case
Research linking emotional connection with outsized customer value and growth (beyond satisfaction) underpins this approach.
Intent Tale Data Insight: Campaign ROI
Our internal analysis of over 100 client campaigns reveals a clear pattern:
Campaigns that used a dedicated ‘Joy/Hope’ appeal in the top-of-funnel (TOFU) saw an average 20% higher share rate and 15% higher landing page time-on-page than control groups.
Conversely, campaigns focusing on ‘Security/Calm’ in the post-onboarding phase saw a 15% higher six-month customer retention rate over campaigns focused solely on product features. We use our own data to validate the frameworks we teach.
The 5-Step Emotional Marketing Framework
1) Feel-first research: persona + moment
Stop guessing. Go listen.
- Who are we helping right now? (role, segment, ACV)
- What moment are they in? launch • lull • crisis • switch
- What do they care about, fear, or hope for?
Ask: “What would make next month a win?” and “What keeps you up at 2 a.m.?” - How to learn: quick surveys, social listening, review mining, and support chats.
Pull exact phrases into your copy.
Artifact: 1-page Persona Snapshot
| Field | What to fill | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Job title + team | Marketing Manager, D2C |
| Pains / Hopes | Top 3 each (use their words) | “Low repeat buyers” / “Want loyal fans” |
| Moment | Launch / Lull / Crisis / Switch | Switch (new ESP) |
| Decision Triggers | Events that cause action | Q4 sales dip; new target |
| Channels | Where they hang out | LinkedIn, YouTube, Email |
| Proof They Trust | What convinces them | Case studies, peer quotes |
| “Win” This Month | Clear, small outcome | +15% repeat orders |
2) Choose the core emotion + job-to-be-done
Pick one feeling to amplify and the progress it unlocks.
- Emotion ideas (Plutchik / Maslow): belonging, security, pride, hope, resolve, curiosity…
- Motivator shortcut (HBR): feel secure, belong, stand out, and have confidence in the future.
- Rule: If your asset “works” with a different emotion, it’s not tight enough.
Quick map
| Chosen Emotion | Why it fits the persona | Job-to-be-done (this month) | Example line |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | They fear churn after the switch | Predictable onboarding in 14 days | “Here’s your 14-day zero-stress plan.” |
| Belonging | They want peers and proof | Join a cohort of 25 D2C leads | “Build with marketers like you.” |
| Pride | They need a visible win | Ship 3 high-retention Reels | “Claim your next milestone.” |
3) Build the story + values-backed offer
Stories create meaning. Offers create movement.
- Story arc: Hook → Tension → Turn → Outcome (make it about the customer).
- Offer: Give something useful now (checklist, calculator, teardown, cohort invite).
- Show your values: customer wins, behind-the-scenes, real people and places.
Creative cues
| Cue | Do | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Visuals | Real photos > stock; faces, hands, close-ups | Feels human and trustworthy |
| Color | Blue = trust • Yellow = optimism • Red = urgency/excitement | Sets the mood instantly |
| Audio & Pace | Simple motif, natural pauses | Space lets the feeling land |
| Focus | One emotion per asset, one CTA | Clarity improves response |
Inspiration
- Nike (resolve), Dove (belonging), Google Year in Search (shared meaning), Spotify Wrapped (pride/identity)
4) Design the experience + distribution
Match emotion → format → channel → CTA.
Where each emotion shines
| Emotion | Great moments | Best formats |
|---|---|---|
| Care | Crisis comms, service updates | Founder note, FAQ video, SMS alert |
| Joy | Launches, milestones | Hero video + cut-downs, UGC montage |
| Nostalgia | Holidays, anniversaries | Carousels, short docs, email stories |
| Belonging | Community drives | Member reels, live AMAs, cohort pages |
| Security | Switching, onboarding | Step-by-step guide, ROI calculator |
CTA alignment
| Emotion | Offer | CTA copy |
|---|---|---|
| FOMO / Urgency | Limited-time webinar/waitlist | “Claim your spot now.” |
| Belonging | Cohort/community invite | “Join the cohort.” |
| Security | Onboarding guide / ROI calc | “See the plan.” |
Delivery checklist
- UTMs set • mobile-first • fast load • accessible captions • one scroll-proof CTA section
5) Test, measure, and learn
Feelings are squishy; results aren’t.
A/B testing plan
| Test one lever | Examples | Success signal |
|---|---|---|
| Opening line | Question vs. bold claim | ↑ Hook retention (3s) |
| Image/thumbnail | Face close-up vs. product | ↑ Clicks/plays |
| CTA phrasing | “See the plan” vs. “Start now.” | ↑ CTR to next step |
| Color cue | Blue vs. Yellow frames | ↑ Saves/time on the page |
What to read (weekly → monthly)
| Type | Metrics | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Quality (weekly) | Saves, shares, replies, time on page, scroll depth, sentiment | Shows if the emotion landed |
| Pipeline (monthly) | Influenced opps, win-rate delta, deal velocity, LCV lift | Shows real business impact |
| Survey | “How did this make you feel?” (word list from chosen emotion) | Gives direct emotional feedback |
Keep / Kill Rule
Kill variants performing < 80% of the control after a fair read. Double down on winners.
One-week sprint
| Day | Action |
|---|---|
| Mon | Brief |
| Tue | Creative V1 |
| Wed | Launch test |
| Thu | Read signals |
| Fri | Iterate & promote |
Mastering Emotional Marketing on a Small Budget (The Human Advantage)
You don’t need a Coca-Cola budget to win hearts; you just need to be human. For small teams and lean startups, your advantage is authenticity. You can skip the glossy ads and go straight to the soul. This is how you apply the Emotional Framework with a small budget:
Low-Cost Tactics to Spark Big Feelings
| Tactic | What to Do Now (Actionable Step) | Emotional Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Tell Real Stories (Not Pitches) | Instead of “best features,” share a customer’s before-and-after journey using names (with permission), emotions, and real photos. Stories create memories that stick. | Hope, Resolve, Pride |
| Surprise & Delight | Send a handwritten thank-you card with a random discount or a small, unexpected freebie in your next 10 orders. People don’t forget the unexpected good stuff. | Joy, Surprise, Belonging |
| Show the Realness | Use your phone to film the imperfect, passionate process: the late-night prep, the messy desk, the genuine team moment. Transparency is your secret weapon; it builds trust. | Trust, Authenticity, Security |
| Create Community | Start a private customer group (Facebook, WhatsApp, or Slack) and ask for genuine product feedback. Make them feel part of something, not just a customer base. | Belonging, Esteem |
Technical Setup: How to Measure Emotion in GA4
Feelings are squishy; results aren’t. To measure the impact of emotional creativity, we must track behavior that indicates deeper engagement:
Emotional Score Event: Set up a custom event tag in GA4 that fires only when a user scrolls below 80% of a campaign landing page or spends over 90 seconds on a key piece of emotional content. This behavioral signal suggests the message resonated deeply, translating feeling into attention.
Branded Search Lift: Track the volume of organic searches for your brand name (unaided recall) in the weeks immediately following a major emotional campaign push. A significant lift indicates successful brand recall and emotional resonance.
Executing emotional marketing campaigns
Case: Wildlense Eco Foundation “Wildlife Warriors”
Context: Traditional ads underperformed with purpose-driven audiences.
Objective: Make conservation personally meaningful to grow awareness, donations, and volunteer action.
Strategy
Storytelling: everyday “wildlife warriors”; true, specific, human.
Triggers: breathtaking wildlife + calm, hopeful score → pride + responsibility.
Shared values: show real community work; avoid slogans.
Credibility: aligned creators; on-site footage and before/after “receipts.”
Distribution
Hero film, social cut-downs, creator collabs, email features, donation/volunteer LP.
Results
Campaign reporting showed ~25% awareness lift and ~30% donation increase during the push; most-saved posts spotlighted local “warriors.”
Takeaways
Pick one emotion, tell one tight story, pair with one clear action, and show visible proof.
Case: EcoCycle “Harit Bharat”
Context: Eco-friendly brand targeting 25–45, skeptical of generic ads.
Approach: Stories of real people choosing sustainable swaps; nostalgic music + Indian landscape visuals; creator partners who live the values.
Outcome: Campaign reporting showed ~30% awareness lift and ~60% sales uplift during the period; customers cited EcoCycle’s mission as the reason to buy.
Lesson: Shared values + sensory cues turn belief into behavior.
For a deep dive into an iconic example of emotional storytelling, see our analysis: Psychological Advertising Case Study: Amul’s Brand Story.
B2B vs. B2C: Different Emotions, Different Goals
The emotion you choose must align with the customer journey stage and the audience:
| Audience | Primary Focus | Go-To Appeals (Examples) |
| B2C (Consumer) | Identity, Aspirations, and Immediate Gratification. | Joy, Nostalgia, Belonging, Curiosity, Excitement. (e.g., making you feel part of a trend) |
| B2B (Business) | Risk Mitigation, Professional Validation, and Long-Term Security. | Security/Calm, Resolve/Determination, Pride, Trust. (e.g., making your job easier, making you look smart) |
7 Core Emotional Appeal → content format → CTA map
| Emotion Used | Best Content Formats | Suggested CTA | Micro-copy Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOMO / Urgency | Limited-time ads, live launch webinar, waitlist page | Claim your spot now | “Seats close tonight; grab yours in 2 clicks.” |
| Belonging / Community | Cohort invite, community post, customer montage | Join the cohort | “Build with founders who ship weekly.” |
| Security / Calm | Onboarding guide, ROI calculator, assurance banner | See the plan | “Sleep better with a predictable pipeline.” |
| Pride / Achievement | Before-and-after case clip, milestone email, leaderboard | Get your score | “See how you rank, then unlock what’s next.” |
| Curiosity / Surprise | Teaser video, pattern-break ad, myth-vs-fact post | Show me the fix | “Most teams miss this one step, do you?” |
| Nostalgia | Throwback creative, seasonal email, founder story | Bring it back | “Back to the simple playbook that still works.” |
| Resolve / Determination | Turnaround case, 30-day challenge, roadmap post | Let’s get you back on track | “Tough quarter? Here’s the path forward.” |
| Joy / Hope | Launch reel, wins carousel, product surprise | See what’s possible | “This is what great feels like, start here.” |
Building emotional connection
Why connection beats features
People decide fast, then justify.
Feelings make memories sticky.
Shared values make brands feel like “mine.”
Emotional values in the wild
Joy: moments of happiness (e.g., Coca-Cola).
Freedom: the open-road identity (e.g., Harley-Davidson).
Belonging: communities that see you.
Pride: “I did it” stories that motivate action.
HBR’s “Emotional Motivators” list
| I am inspired by a desire to… | How brands can leverage this |
|---|---|
| Stand out from the crowd | Help customers express a unique identity; make them feel special or different |
| Have confidence in the future | Paint a positive vision of what’s ahead; reduce uncertainty through storytelling |
| Enjoy a sense of well-being | Offer peace of mind, comfort, and emotional balance through messaging and experience |
| Feel a sense of freedom | Enable choice and independence; remove friction from decision-making or lifestyle |
| Feel a sense of thrill | Create excitement or anticipation through campaigns, events, or product experiences |
| Feel a sense of belonging | Build community, show shared values, and highlight social connections with others |
| Protect the environment | Align with sustainability; empower customers to take positive actions for the planet |
| Be the person I want to be | Encourage personal growth, aspirations, and empowerment through brand storytelling |
| Feel secure | Provide stability, reliability, and consistency in both message and product |
| Succeed in life | Celebrate progress, impact, and meaning beyond material or status-based wins |
Source: “The New Science of Customer Emotions,” Harvard Business Review, Nov 2015
Community & identity (the Harley lesson)
Identity isn’t a by-product; it’s a strategy. When product, purpose, and people align, community compounds; drift from your core, and connection erodes. Realignment restores trust.
Measuring the success of emotional campaigns
KPIs to track weekly
Brand Recall Score: aided/unaided recall from quick polls.
Sentiment Analysis: tonal trends from reviews/social (track net positive %).
Qualitative Signals: “How did this make you feel?” word clouds; save/share comments.
Behavioral Lift: repeat visits, branded search volume, direct traffic (“dark social”).
Pipeline Impact: influenced opportunities, win-rate change, deal velocity, and retention.
Lifetime Customer Value (LCV): LCV before vs. after campaign cohorts.
Emotional brand recall score
- How: 2-question on-site or post-view poll (unaided + aided recall).
- Target: lift vs. control creative.
- Decision: keep winners for brand-level spend.
LCV lift by campaign cohort
How: compare the Lifetime Customer Value of post-campaign cohorts vs. the prior three cohorts (same segment).
Decision: green-light future spend on the appeal that drives durable value, not just CTR.
Simple reporting table
| Metric | How to calculate | Tooling | Decision it informs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Recall Score | % who recall your brand unaided/aided | Polls, on-site surveys | Top-of-funnel resonance |
| Sentiment (net +) | (Positive − Negative) ÷ Total mentions | Listening tools | Tone/creative direction |
| Save/Share Rate | Saves + Shares ÷ Impressions | Platform analytics | Story strength |
| Influenced Opps | Opps touched by the campaign | CRM + UTMs | Revenue impact |
| Win Rate Δ | Win% post − Win% pre | CRM | Proof & objection-handling |
| LCV Lift | LCV (cohort post) ÷ LCV (cohort pre) | Billing/analytics | Long-term value |
Ethical Execution and Creative Compliance
Emotional marketing requires vigilance. To ensure your campaigns are both trustworthy and effective, adhere to these ethical boundaries and creative rules:
1. Ethical Boundaries and Trustworthiness
Trust is the foundation of emotional connection. Your practices must be transparent and respectful:
Avoid Manipulation: Do not fabricate urgency, outcomes, or social proof (fake testimonials or results).
Respect Vulnerable Groups: Avoid fear-mongering or shaming. If using fear appeals, ensure they are appropriate, and always provide opt-outs and safety language.
Dignity and Consent: Represent people with dignity. Get explicit consent for names, quotes, stories, and images, and respect all takedown requests.
Honesty in Claims: Back every promise with delivery. When using sensitive themes (like health or finance), include plain-language disclaimers and link to help resources.
Transparency: Make opt-outs and unsubscribe methods clear and easy.
2. Creative Compliance Checklist
Once the ethical foundation is secure, apply these rules for maximum creative clarity and impact:
| Rule | Purpose |
| One Emotion Per Asset | Clarity: Prevents the message from feeling confused or diluted. |
| Real Faces > Stock | Authenticity: Makes the content feel human and trustworthy. |
| One Clear Arc | Storytelling: Follow the natural progression: hook → tension → turn → outcome. |
| One Unmistakable Proof Point | Credibility: Use a single stat, clip, or screenshot to validate your claim. |
| One Direct CTA | Action: Directs the user to the next clear step, minimizing decision fatigue. |
Credits & further reading
- Emotional marketing creates lasting connections
- Emotional Marketing and Psychological Ads
Neuroscience – Reviews on the amygdala’s role in emotional memory and consolidation.
- Storytelling Frameworks to drive loyalty
- McGaugh, J. L. (2004). The amygdala modulates the consolidation of memories of emotionally arousing experiences. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 27, 1–28.
Frequently Asked Questions About Emotional Marketing
The following section addresses the most common questions about emotional marketing strategy, ethics, and implementation.
What is emotional marketing?
Emotional marketing is designing brand moments that trigger meaningful feelings (like joy, security, or belonging) so people remember, trust, and act. The core rule is to lead with one emotion per campaign, backed by a true story and proof.
What are the best examples of B2B emotional marketing?
The most effective examples are security-led onboarding that emphasizes predictability and low risk, resolve-themed turnaround stories in down quarters, and pride-based milestone programs (e.g., customer wins or certifications) that lift retention and expansion.
How do leading brands use emotional advertising?
They select a single emotion, tell a specific and true story, show clear proof (stats, screenshots, or clips), and meticulously align the creative format and Call-to-Action (CTA) with that feeling. They then measure brand recall, sentiment, and pipeline impact.
What emotional appeals work best in B2B vs B2C?
For B2C, appeals like joy, nostalgia, and belonging are best for launches and community-building. For B2B, focus on security, resolve, and professional pride to reduce perceived risk and celebrate professional success.
How do I measure emotional marketing ROI?
You measure ROI by tracking behavioral lifts and pipeline impact. Key metrics include brand recall lift, net sentiment score, save/share rate, influenced opportunities, win-rate change, deal velocity, and the Lifetime Customer Value (LCV) lift by campaign cohort.
Is emotional marketing ethical?
Yes, emotional marketing is ethical when it is truthful, consent-based, and dignified. You must avoid fear-mongering, fabricating urgency, or manipulating vulnerable groups. Always provide clear opt-outs and ensure you deliver on every promise.
Which emotion should I choose for a launch?
Lead with joy or hope to create momentum, and pair it with belonging if you are building a cohort or community. Always keep the CTA positive and forward-looking, using phrases like “See what’s possible.”
What is the fastest way to start with emotional marketing?
The quickest start is to publish one customer story with a useful offer and a single CTA. Use real photos and a short proof clip. The test-and-learn approach means you should test two opening lines and two CTAs within the first week.

















One Response
I haven’t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I’ll add you back to my daily blog list. You deserve it my friend 🙂